In modern medical testing and clinical diagnosis, blood tests are crucial for obtaining information about human health. Medical disposable blood collection needles are indispensable basic tools in this process. As single – use medical consumables, blood collection needles play a key role in preventing cross – infection and ensuring patient safety with their safe and convenient features. This article will elaborate in detail on the classification, usage methods and precautions, advantages as single – use medical consumables, and proper disposal of medical disposable needles.
Classification of Blood Collection Needles
Medical blood collection needles can be divided into various types according to different design and functional requirements, and each type is suitable for specific blood collection scenarios.
Classification by Blood Collection Method
Straight – insertion Blood Collection Needles: This is the most common type of blood collection needle. The needle head is straight, and blood is collected by manually inserting it directly into the vein. Straight – insertion blood collection needles have a simple structure and are easy to use. They are suitable for routine venous blood collection, especially in places such as outpatient clinics and physical examination centers where high blood collection efficiency is required. Their needle heads usually adopt a sharp bevel design, which can reduce the resistance during puncture and relieve patients’ pain.
Butterfly – wing Blood Collection Needles: Also known as “scalp – needle – type “, they get their name from the hose and needle handle that resemble butterfly wings. After a successful puncture, this type of needle can be connected to a blood collection tube through the hose, making it convenient to adjust the position. It is especially suitable for patients with thin veins, difficult – to – fix veins, or those who require long – term blood collection, such as infants, the elderly, or patients undergoing long – term hemodialysis. The flexibility of butterfly – wing needles gives them an advantage in complex environments.
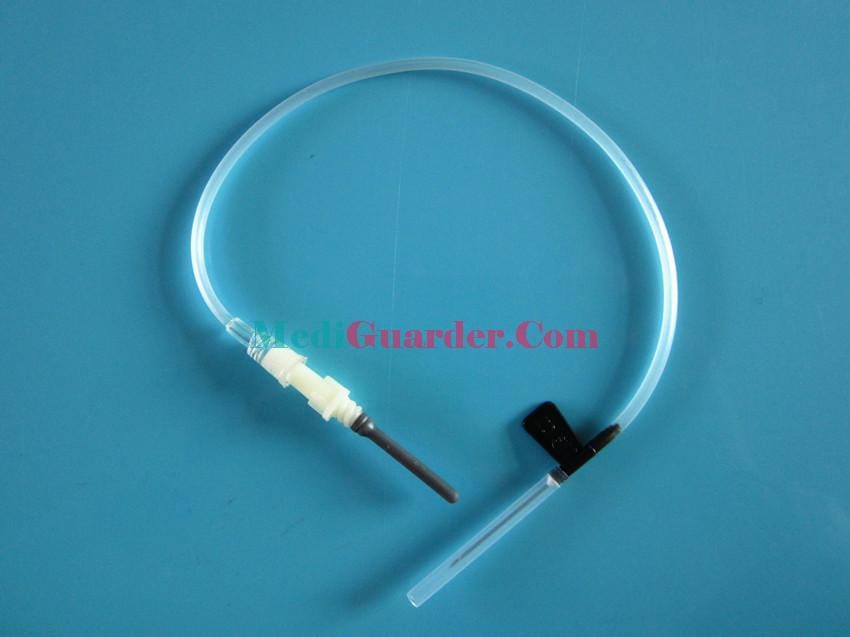
Classification by Needle Gauge
The gauge of blood collection needles is expressed in “G” (Gauge). The larger the number, the thinner the needle. Common gauges include 21G, 22G, 23G, 25G, etc. Needles with a gauge of 21G – 22G are thicker and are suitable for blood collection for tests that require a large amount of blood or have high blood viscosity, such as biochemical examinations and blood routine tests. Needles with a gauge of 23G – 25G are thinner, cause less damage to blood vessels, and result in less pain. They are often used for blood collection from children, peripheral blood collection, or for patients who are more sensitive to pain.
Classification by Functional Characteristics
Safety Blood Collection Needles: To reduce the risk of needle stick injuries to medical staff during blood collection, safety needles were developed. These needles are usually equipped with special safety devices, such as automatic needle retraction and automatic needle cap locking. After blood collection is completed, by pressing a specific button or triggering the mechanism, the needle will quickly retract into the protective sleeve, effectively preventing accidental stabbings and greatly enhancing the safety of blood collection operations.
Anticoagulant – coated Blood Collection Needles: Some blood collection needles are pre – coated with anticoagulants or heparin inside, which can prevent the collected blood from clotting in a short time and ensure the quality of blood samples. They are suitable for blood collection for tests such as hemorheology and coagulation function.
Usage Methods
Usage Methods
Preparation: Before blood collection, medical staff should wear protective equipment such as medical gloves and masks, check whether the packaging of the blood collection needle is intact, and confirm that the product is within the validity period. At the same time, prepare appropriate blood collection tubes. Select different types of blood collection tubes (such as anticoagulant tubes, coagulation – promoting tubes, etc.) according to the test items, and correctly attach patient information labels to the blood collection tubes.
Patient Preparation: Explain the purpose and process of blood collection to the patient to relieve their nervousness. Help the patient choose a suitable blood collection position, usually sitting or lying down, and expose the blood collection site, such as the elbow vein. Disinfect the blood collection site with iodine – containing disinfectant or alcohol. The disinfection range should be no less than 5 cm in diameter, and wait for the skin to dry naturally before performing the puncture.
Puncture and Blood Collection: Take the straight – insertion needle as an example. The medical staff should fix the patient’s skin at the blood collection site with the left hand, hold the needle with the right hand, and quickly insert it into the vein at an angle of 30° – 45°. After seeing the return of blood, insert the other end of the needle into the blood collection tube, and the blood will automatically flow into the tube under negative pressure. If multiple tubes of blood need to be collected, change the blood collection tubes in a specific order until the required amount of blood is collected. For butterfly – wing needles, fix the needle handle after a successful puncture, and then connect the blood collection tube for blood collection.
Completion of the Operation: After blood collection is completed, quickly pull out the needle, and press the puncture site with a sterile dry cotton swab for 5 – 10 minutes until the bleeding stops. Immediately place the used needle into a special sharp – container to avoid secondary contamination.
Precautions
Strict Aseptic Operation: The blood collection process must adhere to the principle of asepsis to prevent patient infection caused by improper operation. Reusing blood collection needles is strictly prohibited. Even for the same patient, a new disposable blood collection needle must be used.
Select the Appropriate Blood Collection Site: Avoid collecting blood from areas with skin damage, infection, or edema. For patients with long – term infusion, blood should be collected from the limb opposite to the infusion side to ensure the accuracy of blood samples.
Pay Attention to the Patient’s Reaction: Closely observe the patient’s complexion, expression, etc. during blood collection. If the patient shows discomfort symptoms such as dizziness and palpitations, stop blood collection immediately, let the patient lie down and rest, and provide corresponding treatment.
Properly Dispose of Sharps: Used blood collection needles are sharps and pose a stabbing risk. They must be placed in a special puncture – proof and leak – proof sharp – container. It is strictly prohibited to discard them casually or mix them with other medical waste.
Advantages of Single – use Medical Consumables
As a typical single – use medical consumable, blood collection needles have many irreplaceable advantages. First, they can effectively prevent cross – infection. If traditional reusable needles are not thoroughly cleaned and disinfected, pathogens are likely to remain, leading to cross – infection between different patients. The feature of disposable blood collection needles, which come in individual packaging and are discarded after use, fundamentally eliminates this risk. Second, disposable needles are convenient to use. Without complex cleaning, disinfection, and storage processes, they save a lot of labor and time costs and improve medical work efficiency. In addition, the production standards for disposable needles are strict, and their quality is stable, providing a reliable guarantee for accurate blood testing.
Proper Disposal of Medical Disposable Needles
Medical disposable needles are classified as infectious medical waste and have the characteristics of sharps, so their disposal must follow strict regulations. The used medical disposable needles should be immediately placed in a special puncture – proof and leak – proof sharp – container, which should be placed in a convenient and safe location. When the sharp – container is filled to 3/4 of its capacity, it should be sealed in a timely manner, labeled with information such as the type of medical waste, the department where it was generated, and the generation date. The sealed sharp – container will be transported by special personnel to the hospital’s medical waste temporary storage area, which should be equipped with facilities to prevent rats, mosquitoes, flies, and cockroaches and be regularly disinfected. Finally, the medical waste will be harmlessly treated by qualified disposal units using professional methods such as high – temperature incineration to ensure that pathogens are completely killed and to prevent environmental pollution and disease transmission.
Conclusion
Although medical disposable needles seem small and simple, they play a vital role in medical diagnosis and patient safety. Understanding their classification, mastering the correct usage methods and precautions, and properly disposing of medical waste are not only the responsibilities of medical staff but also related to the health and safety of every patient. With the continuous development of medical technology and the increasing emphasis on medical safety, the design and management of disposable needles will become more scientific and perfect, providing a solid guarantee for the development of the medical cause.
 China Disposable Medical Supplies, Medical Consumables Supplier
China Disposable Medical Supplies, Medical Consumables Supplier
WhatsApp
Scan the QR Code to start a WhatsApp chat with us.