The disposable medical syringe with needle is an indispensable basic medical device in the modern medical field. Its original design purpose is to avoid cross – infection through single use, while ensuring the accuracy and safety of injection, puncture and other operations. This article will introduce its classification, uses and standardized usage methods in detail, providing a reference for medical practice.
Classification of disposable medical syringes with needles
Disposable medical syringes with needles can be classified in various ways, mainly based on structure, capacity and characteristics of the disposable medical needle.
According to the structure, they can be divided into ordinary type and safety type. The ordinary syringe is composed of a syringe barrel, a piston, a push rod and a disposable medical needle. It has a simple structure and is suitable for routine injection operations. The safety syringe, on the basis of the ordinary type, is added with a needle protection device, such as an automatic retractable needle and a shield – type protective cover. It can quickly cover the needle after use, greatly reducing the risk of medical staff being stabbed, and is especially suitable for medical operations dealing with infectious patients.
According to the capacity, common specifications include 1mL, 2mL, 5mL, 10mL, 20mL, 50mL and 100mL. Small – capacity syringes (1 – 5mL) are mostly used for intradermal injection, subcutaneous injection, intramuscular injection and intravenous push of small – dose drugs; medium and large – capacity syringes (10 – 100mL) are mainly used for intravenous infusion, extraction of a large amount of blood or liquid medicine and other scenarios.
According to the characteristics of the disposable medical needle, it can be classified according to the needle diameter (gauge) and length. The needle diameter is usually represented by a number. The larger the number, the thinner the diameter. For example, a 4.5 – gauge needle has a diameter of 0.45mm and is suitable for intradermal injection; a 7 – gauge needle has a diameter of 0.7mm and is often used for intramuscular injection. The length of the needle also varies according to the purpose. Short needles (such as 8mm) are suitable for subcutaneous injection, and long needles (such as 30mm) are mostly used for intramuscular injection.
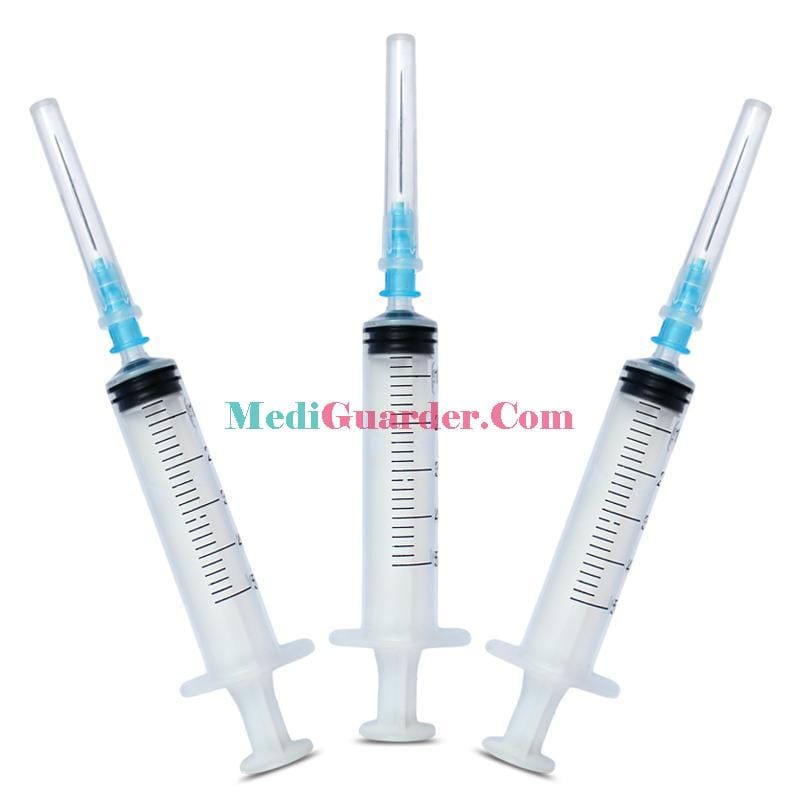
Uses of disposable medical syringes with needles
Disposable medical syringes with needles are widely used in the medical field, covering many links such as diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
In terms of injection administration, it is an important carrier for drugs to enter the human body. Intradermal injection is often used for allergy tests, preventive vaccination, such as penicillin skin test; subcutaneous injection is suitable for the administration of drugs such as insulin and low – molecular heparin, and the drugs are slowly absorbed through the subcutaneous tissue; intramuscular injection is used for drugs that are not suitable for oral or intravenous injection, such as some antibiotics, which can be quickly absorbed through the blood vessels rich in muscles; intravenous injection can make drugs directly enter the blood circulation and exert their effects quickly, which is suitable for first aid, supplementing body fluids and nutrition, etc.
In diagnostic operations, syringes can be used to extract blood samples for blood routine, biochemical and other examinations, and also to extract pleural effusion, peritoneal effusion, etc. for pathological analysis, providing a basis for disease diagnosis.
In addition, in infusion therapy, medium and large – capacity syringes can be used with infusion sets for intravenous infusion; in some minimally invasive surgeries, they can also be used for flushing wounds, injecting contrast agents, etc.
Usage methods of disposable medical syringes with needles
Standardized use of disposable medical syringes with needles is the key to ensuring medical safety. The specific steps are as follows:
Preparation before operation: First, check whether the syringe package is intact, confirm that it is within the validity period, and there is no damage, air leakage, etc. At the same time, medical staff must strictly implement hand hygiene and wear protective equipment such as sterile gloves and masks. According to the purpose of injection and the patient’s condition, select a syringe with appropriate capacity and needle specification and corresponding drugs.
Extracting liquid medicine: After disinfecting the drug ampoule or vial, pierce it with the syringe needle and slowly extract the liquid medicine. During the extraction process, attention should be paid to avoiding the generation of bubbles. If there are bubbles, gently push the piston to discharge the bubbles.
Injection operation: Select the appropriate injection site according to the type of injection and disinfect it. Intradermal injection is often selected in the lower segment of the volar side of the forearm, and the needle insertion angle is parallel to the skin; subcutaneous injection is mostly selected in the lower edge of the deltoid muscle of the upper arm, and the needle insertion angle is about 30 – 40°; intramuscular injection is often selected in the gluteus maximus, deltoid muscle, etc., and the needle insertion angle is about 90°; for intravenous injection, it is necessary to find a suitable vein, fix the needle after successful puncture, and slowly push the liquid medicine.
Post – operation treatment: After the injection, quickly pull out the needle and press the puncture point with a sterile cotton swab for a moment. Then, put the used syringe (including the disposable medical needle) into a special sharps box, and it is strictly forbidden to discard it at will to prevent pollution and accidental stab wounds.
In conclusion, the reasonable classification and correct use of disposable medical syringes with needles are crucial to ensuring medical quality and patient safety. Medical personnel should be proficient in their relevant knowledge and strictly operate in accordance with the operating procedures to maximize their effectiveness in medical practice.
 China Disposable Medical Supplies, Medical Consumables Supplier
China Disposable Medical Supplies, Medical Consumables Supplier
WhatsApp
Scan the QR Code to start a WhatsApp chat with us.