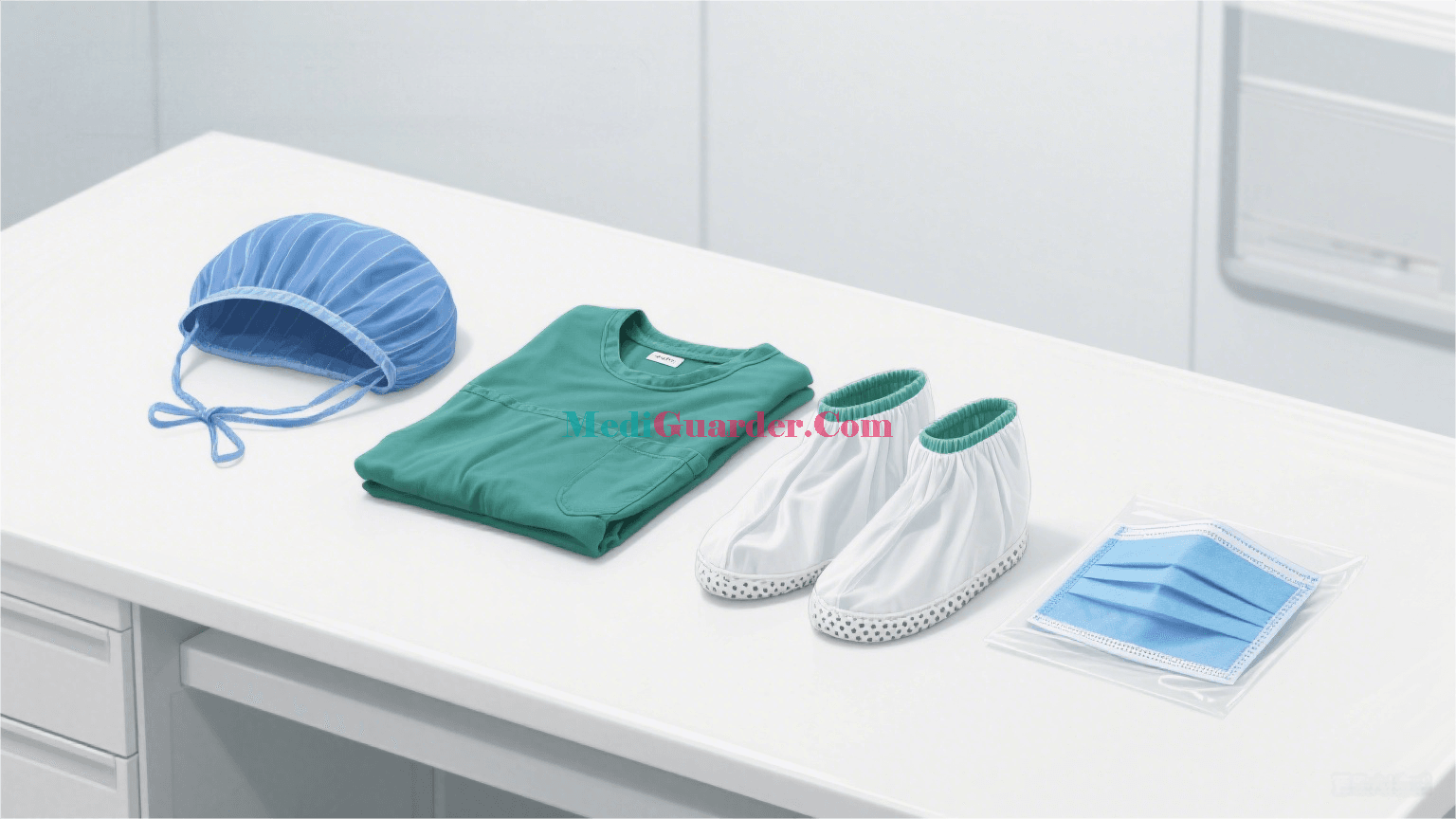
In the modern medical field, infection control is a core link in ensuring patient safety and medical quality. Disposable medical non-woven products, with their excellent barrier properties, breathability, and convenience, have become an important line of defense in preventing cross-infection. This article focuses on four commonly used products: surgical caps, disposable surgical gowns, disposable shoe covers, and disposable masks, and elaborates on their classification, applications, and standard usage methods.
Surgical Caps
Surgical caps are indispensable protective supplies in operating rooms and clean medical environments, mainly used to block the shedding of medical staff’s head hair and dandruff, avoiding contamination of sterile areas.
(1) Classification
According to differences in structure and material, surgical caps can be divided into two types:
Ordinary non-woven dome caps: Made of single or double-layer SMS non-woven fabric, with a hemispherical top and elastic rubber bands at the edges. These caps have a relatively low cost and are suitable for scenarios with moderate cleanliness requirements, such as small outpatient surgeries and dressing changes.
Disposable strip caps: Sewn from spun-bonded non-woven fabric, they are in the shape of a folded strip. When worn, they can completely cover the head and hairline, with air vents designed on the top. Due to their better sealing performance, they are often used in environments with strict sterility requirements such as operating rooms and ICUs.
(2) Applications
In addition to the core function of preventing hair contamination, surgical caps can also protect medical staff’s heads from splashing blood and body fluids, and reduce the risk of contamination of sterile gloves by head sweat. In special areas such as infectious disease wards and fever clinics, wearing surgical caps can reduce the probability of cross-infection between medical staff and patients.
(3) Usage Methods
Clean hands before wearing. Take out the surgical cap, unfold it, and completely cover the head, ensuring that the hairline and the skin behind the ears are covered. For dome caps, the edge of the elastic band should be 紧贴 the jaw; for strip caps, adjust the elastic band to a comfortable position to avoid discomfort caused by over-tightening. After use, they should be treated as infectious waste and must not be reused.
Disposable Surgical Gowns
Disposable surgical gowns are important protective equipment for medical staff during surgeries, and their performance directly affects surgical safety.
(1) Classification
According to the protection level and applicable scenarios, they can be divided into:
Ordinary surgical gowns: Made of spun-bonded non-woven fabric with good breathability, they can only block general dust and a small amount of liquid, and are suitable for low-risk operations such as superficial body surgeries and gynecological examinations.
Reinforced surgical gowns: Key parts (chest, cuffs) are made of SMS composite non-woven fabric, which has hydrostatic pressure resistance and can resist the penetration of blood and body fluids. They are used in medium and high-risk surgeries such as orthopedics and general surgery.
Sterile surgical gowns: Sterilized by ethylene oxide and individually packaged, they are suitable for operations with ultra-high cleanliness requirements such as organ transplantation and heart surgery.
(2) Applications
Surgical gowns form a physical barrier to prevent direct contact between medical staff’s skin and patients’ blood and body fluids, and also prevent microorganisms carried by medical staff from contaminating the surgical wound. The elastic design of the cuffs can fix the position of gloves, preventing gloves from slipping off during surgery.
(3) Usage Methods
Perform surgical hand disinfection before putting on the surgical gown. After opening the sterile package, gently unfold the gown by pinching the inner side of the collar with both hands, avoiding touching the gown body. Insert both arms into the sleeves, and ask others to help fasten the back ties, ensuring that the area below the waist is completely covered. After putting on sterile gloves, fold the cuffs outward to the outside of the glove cuffs and fix them. After the surgery, first take off the gloves, then fold the surgical gown from the inside out to take it off, avoiding contact with the contaminated surface.
Disposable Shoe Covers
Disposable shoe covers are an important means to control ground contamination in medical environments, which can effectively block the transmission path of microorganisms carried on the soles.
(1) Classification
According to material and function, they can be divided into:
Ordinary non-woven shoe covers: Made of spun-bonded non-woven fabric, they are lightweight and breathable, with no anti-slip treatment on the bottom, and are suitable for dry environments such as outpatient clinics and laboratories.
Anti-slip shoe covers: The bottom is compounded with PE film or rubber particles, having anti-slip performance, and are used in areas prone to contact with liquids such as operating rooms and sterile supply centers.
High-top shoe covers: The height exceeds the ankle, made of waterproof non-woven fabric, which can protect the lower legs from contamination, and are often used in high-risk areas such as infectious disease wards and fever clinics.
(2) Applications
Shoe covers are mainly used to prevent bacteria carried on the soles of medical staff from contaminating the ground in clean areas, and also to avoid contamination of medical staff’s shoes by patients’ body fluids and blood. In public health emergencies, shoe covers are an important part of personal protective equipment (PPE) and can reduce the risk of environmental transmission.
(3) Usage Methods
Before wearing, check that the shoe covers are not damaged. Step into the shoe covers with both feet respectively, pull the upper opening of the shoe covers above the ankles, ensuring that the heels are completely covered. Be careful when walking on wet floors to prevent slipping. After use, handle them according to medical waste classification. If the shoe covers are damaged, they must be replaced immediately and the contaminated area should be disinfected.
Disposable Masks
Disposable masks are core respiratory protection products, which can effectively block droplet transmission and play a key role in epidemic prevention and control.
(1) Classification
According to protection performance and applicable scenarios, they are mainly divided into:
Ordinary medical masks: Composed of a three-layer non-woven structure, with the outer layer being waterproof, the middle layer for filtration, and the inner layer for moisture absorption. They can filter larger particle aerosols and are suitable for daily protection in ordinary medical environments.
Medical surgical masks: They have good bacterial filtration efficiency (≥95%) and fluid resistance, can effectively block splashing blood and body fluids, and are used in invasive operations such as surgeries and punctures.
Medical protective masks (N95/KN95): Using the principle of electrostatic adsorption, they have a filtration efficiency of ≥95% for non-oily particles and strong airtightness. They are suitable for high-risk operations involving contact with patients with respiratory infectious diseases.
(2) Applications
Masks can filter microorganisms, droplets, and particles in the air, which can not only protect medical staff from infection but also prevent patients from being contaminated by bacteria carried by medical staff. During the prevail of infectious diseases, wearing masks is an important measure to block community transmission.
(3) Usage Methods
Wash hands before wearing. For ordinary medical masks and surgical masks, distinguish the front and back (the dark color is outward, and the metal strip is upward), hang the ear loops on both ears, press the metal strip to fit the bridge of the nose, and stretch the mask downward to cover the mouth, nose, and chin. For medical protective masks, a fit test is required: cover the mask with both hands, and when exhaling, if you feel the mask slightly bulge without air leakage, it means the wearing is qualified. The service life of a mask is generally no more than 4 hours, and it must be replaced immediately if contaminated or damp.
Disposable medical non-woven products are an important part of the medical safety system. Correct selection and use of these products are of great significance for reducing the rate of nosocomial infections and ensuring the safety of doctors and patients. Medical staff should reasonably select them according to the risk level of operations and strictly abide by the wearing standards. At the same time, relevant institutions should strengthen quality management to ensure that products meet national standards and jointly build a medical safety defense line.
 China Disposable Medical Supplies, Medical Consumables Supplier
China Disposable Medical Supplies, Medical Consumables Supplier

WhatsApp
Scan the QR Code to start a WhatsApp chat with us.