In the modern medical system, disposable medical supplies have become indispensable tools in clinical care due to their convenience and safety. As an important part of them, disposable medical adult urinary bags are widely used in the care of patients undergoing postoperative rehabilitation, those who are bedridden for a long time, have limited mobility, or suffer from urinary system diseases. They not only provide convenience for patients and reduce the nursing burden but also effectively prevent cross – infection and improve the quality of care. However, improper use and disposal may lead to a series of problems, such as infection and leakage, which can affect patients’ health and even cause environmental pollution. Therefore, it is crucial to master the correct usage methods, precautions, and the disposal of medical waste related to medical urinary bags.
Usage Methods of Medical Urinary Bags
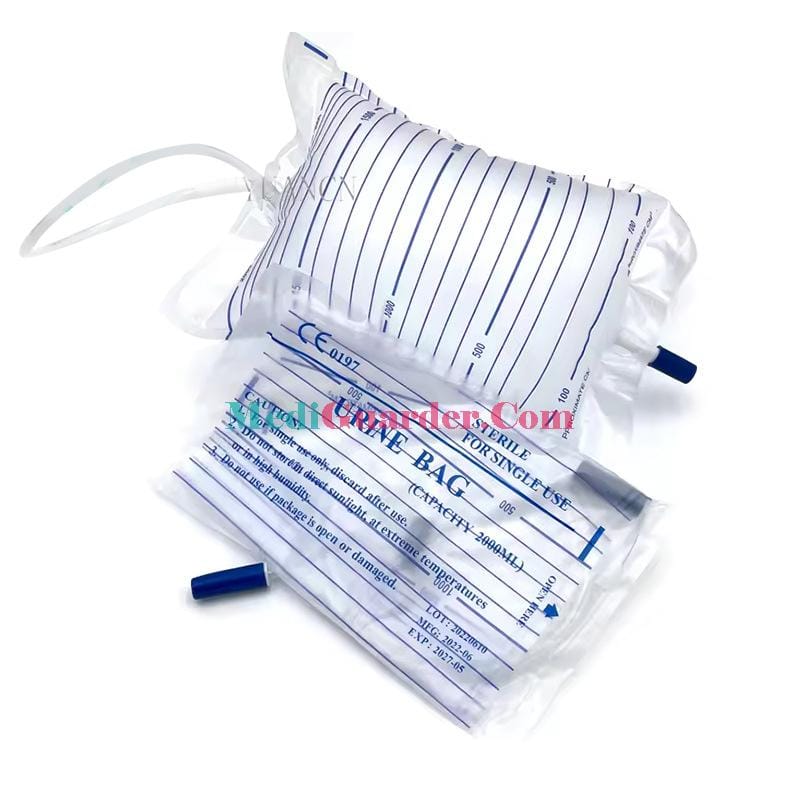
Disposable medical adult urinary bags are mainly composed of components such as the urine collection bag, drainage tube, anti – reflux device, and urine discharge valve. Before use, medical staff or caregivers need to make full preparations and strictly follow the principles of aseptic operation. First of all, hand hygiene should be carried out. Wash hands thoroughly with running water and hand sanitizer, or disinfect hands with a quick – drying hand sanitizer to avoid contaminating the urinary bag. Then, carefully check whether the packaging of the urinary bag is intact, and check the production date, expiration date, as well as whether there are any damages, leaks, etc., to ensure the quality of the urinary bag.
When wearing the urinary bag for the patient, an appropriate position should be selected according to the patient’s specific condition. For cooperative patients, a supine or lateral position can be adopted; for patients with limited mobility, assist them in adjusting their posture carefully to avoid excessive pulling or twisting of the drainage tube. Connect the drainage tube of the urinary bag to the patient’s urinary catheter or fistula tube. When connecting, ensure that the interface is tight to avoid urine leakage. After the connection is completed, fix the urinary bag properly on the patient’s bedside or wheelchair. The height should be lower than the level of the bladder to prevent urine backflow and infection. When fixing, pay attention to the right tightness to avoid affecting blood circulation due to being too tight or causing the urinary bag to fall off due to being too loose.
During the use process, closely observe the color, properties, and volume of the urine. Normal urine is light yellow, clear, and transparent. If abnormal conditions such as darkening of urine color, turbidity, flocculent substances, or hematuria are found, the doctor should be informed in a timely manner. At the same time, discharge the urine regularly. When the urine in the urinary bag is two – thirds full, open the urine discharge valve and discharge the urine into the designated container. When discharging, pay attention to avoiding urine splashing. After discharge, close the urine discharge valve to keep the urinary bag clean.

Precautions for the Use of Medical Urinary Bags
Maintaining the cleanliness and tightness of the urinary bag and the drainage system is the key to preventing infection. Clean the vulva and the area around the urethral orifice with warm water and a neutral detergent every day. Male patients should pay attention to cleaning the dirt inside the prepuce, and female patients should wipe from front to back to avoid bringing bacteria from the anus into the urethra. Replace the urinary bag regularly. Generally, according to the patient’s condition and medical advice, replace it 1 – 2 times a week. If the urinary bag is damaged, leaking, or contaminated, replace it immediately. At the same time, ensure that the drainage tube is free of twists and folds and keep it unobstructed to prevent increased pressure in the bladder due to poor urine drainage, which may lead to infection or other complications.
Paying attention to the patient’s comfort and psychological state cannot be ignored. Long – term use of urinary bags may cause discomfort and psychological pressure to patients. Nursing staff should regularly check the skin at the fixed position of the urinary bag to see if there are any pressure sores, allergies, etc., and adjust the fixing method in a timely manner. Communicate more with patients, understand their feelings, provide psychological support and comfort, and help patients establish a positive attitude to cooperate with treatment and care.
In addition, when moving the patient or assisting the patient to turn over, pay special attention to protecting the urinary bag and the drainage tube. First, place the urinary bag properly to avoid pulling and squeezing, and prevent the drainage tube from coming off or urine leakage. During the movement, keep the urinary bag lower than the level of the bladder to prevent urine backflow. For patients with unclear consciousness or restlessness, restraint straps can be appropriately used for protection, but pay attention to the tightness to avoid damaging the patient’s skin.
Correct Disposal of Medical Waste of Disposable Medical Urinary Bags
Disposable medical adult urinary bags belong to infectious medical waste and contain a large number of pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses. If not disposed of properly, it is extremely easy to cause disease transmission and environmental pollution. Therefore, it is necessary to strictly follow the medical waste disposal specifications for disposal.
The used urinary bag should be preliminarily processed in a timely manner. Close the urine discharge valve and discharge the remaining urine into the designated sewage treatment system to avoid random dumping of urine. Then, put the urinary bag into a special yellow medical waste bag to ensure that the bag is free of damage and leakage. When sealing, use the gooseneck sealing method to tie the bag tightly to prevent waste leakage. Paste a label on the outside of the waste bag, indicating the type of medical waste, the department where it is generated, the generation date, and other information.
Medical waste bags should be temporarily stored in the designated medical waste storage room of the hospital. The storage room should be ventilated, and measures should be taken to prevent rats, mosquitoes, flies, and cockroaches. The floor and walls should be regularly cleaned and disinfected. The temporary storage time of medical waste should not exceed 48 hours, and it should be promptly transported and disposed of by a qualified medical waste disposal unit. During the transportation process, special closed transportation vehicles should be used, and measures should be taken to prevent leakage and spillage to avoid environmental pollution.
After receiving the medical waste, the disposal unit will use appropriate methods such as incineration and chemical disinfection to harmlessly treat the disposable medical urinary bags, ensuring the complete elimination of pathogenic microorganisms and eliminating the risk of disease transmission.
The correct use, precautions, and medical waste disposal of disposable medical adult urinary bags are crucial in every aspect. Medical staff, caregivers, patients, and their families should fully understand the relevant knowledge and strictly follow the standardized operation to jointly ensure medical safety and environmental hygiene and create good conditions for the patient’s rehabilitation.
 China Disposable Medical Supplies, Medical Consumables Supplier
China Disposable Medical Supplies, Medical Consumables Supplier
WhatsApp
Scan the QR Code to start a WhatsApp chat with us.